In the era of digital commerce, customer behaviour is constantly changing, so that businesses have to adapt their organizational and technological strategies to tackle emerging demands and seize opportunities. The global pandemic (COVID-19) has created an unparalleled increase in online sale by consumers across the globe. E-commerce sales have doubly increased for each and every type of dealer since the start of the crisis.
For entrepreneurs who want to develop their e-commerce business, it is the time to act now. Customers from across the globe can be seen establishing habits that will last much longer even after the pandemic has gone past, whether a company sells to any other businesses, directly to customers or to both.
Recent studies show that e-commerce sales in the year 2021, are expected to account for 18.1 percent of retail sales worldwide.
The above statistics clearly shows how e-commerce is becoming a more and more important part of global commerce. It’s growing so quickly that it’s expected to make up a whopping 22.0 percent of retail sales worldwide by 2023.
E-commerce is growing in all directions and is becoming an integral part of the consumer experience worldwide.
The key points to be considered for developing an e-commerce business model will depend on the following factors:
- Product or Service: Providing the apt product or service will help fulfil the buyers needs and increase retention.
- Market Place or Own Website: Having your own company website which will represent the products or services you sell directly to the customers or getting into the right market place is also an important factor in developing an e-commerce business model.
- Shipping/Delivery: A plus point to every business e-commerce model is a reliable shipping/delivery service provider. Authentic and timely delivery of products is necessary to keep customers happy. Any online store should be responsible for a shipping providers fulfilment regardless of fault, which will create a valuable partnership.
E-Commerce Business Models:
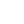
1. Business to Business (B2B): This is a well-known business model where in one business sells its products or services to another business. In this model, the business to whom the products or services are being sold may not be the end user – they could be a reseller as well. Most of the businesses which follow the B2B business model are service providers, but not all of them. Any company using this model can sell anything from physical goods or services.
Examples of B2B Business Model: DropBox, Amazon Business, Xerox, WeWork, Alibaba, Skype etc.
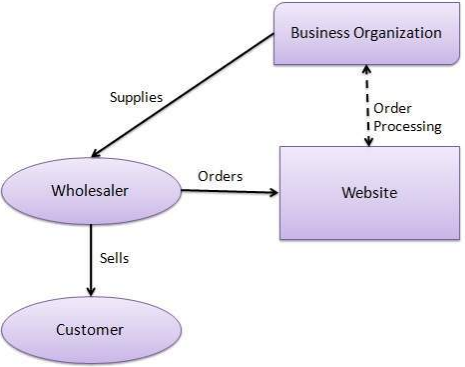
2. Business to Consumer (B2C): This business model is where in businesses sell their products to the end user. This is the most commonly used business model, hence there are many distinctive approaches under this model. Anything a consumer buys in an online store example a household supplies, furniture, entertainment is all part of a B2C transaction. For products which have a lesser value, the decision-making process for a B2C purchase is much shorter than B2B purchase.
B2C pathfinders have used technology like mobile apps and native advertising to remarket directly to their customers which in turn makes their lives easier in the process.
Examples for B2C Business Model: Amazon, Facebook, Walmart, Netflix, Flipkart etc.
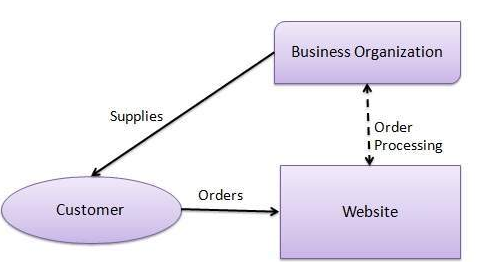
3. Consumer to Consumer (C2C): A C2C business model is also known as online marketplace – which connects consumers to trade products and services and earn money by charging transaction or listing fees. C2C business benefit from self-operating growth by motivating buyers and sellers, but they also face an important challenge – quality control and technology maintenance. This business model also helps consumers sell their assets which include residential property, cars, motorcycles, or even rent a room by publishing information on the website.
Examples for C2C Business Model: e-Bay, Instagram, Facebook, Amazon, etc.
4. Consumer to Business (C2B): This is a forthcoming business model wherein sole proprietors or individuals sell products or services to companies. This business model is still not very known among people but is growing in prevalence. This online business is conducted when the consumer sells goods or services to businesses and it is roughly equivalent to a sole proprietorship serving a larger business.
Additionally, bloggers can connect to businesses that need them and write posts and blogs about their products or services which will add an extra push in selling the same, Influencers can also be hired by businesses to increase their sales. The advantage of using this type of business model is that there is no inventory to manage, no monetary investment and no customer service. These sales are done all at once.
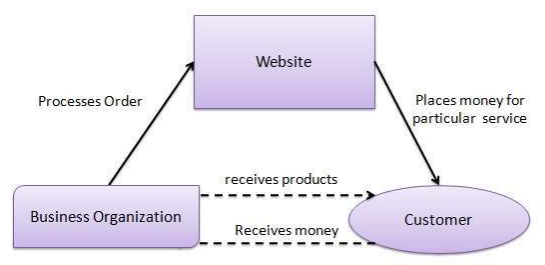
Examples for C2B Business Model: Google, Survey Monkey, A chef blogger who bills a kitchen company for promoting their cooking products on the blog, Photographers who sell their images on e-commerce websites designed for selling images etc.
Delivery Models for Ecommerce Business
1. D2C (Direct to Consumers): The conventional supply chain includes supplier, manufacturer, wholesaler, distributor, and retailer. This business model turned a deaf ear to the conventional supply chain and businesses decided to remove the middlemen such as wholesalers, distributors etc and instead harnessed the power of the cloud and used the right e-commerce method to sell their products and services directly to the end user.
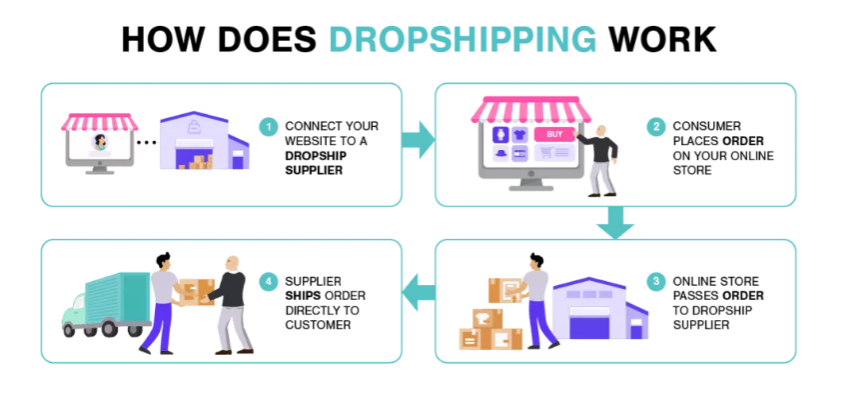
2. Drop Shipping: In recent times, this delivery model has emerged as a brilliant retail fulfilment model for any ecommerce beginners to launch their business with little or no capital. This delivery model allows businesses to market and sell their products online with having any inventory. As and when orders are received by the business the drop shippers purchase the product from the suppliers who then ship the product directly to the consumer.
3. Wholesaling and Warehousing: Wholesaling and Warehousing: The wholesaling and warehousing ecommerce businesses require a lot of investment at the beginning and also, they will need to manage inventory and stock, keep track of customer orders and also the logistics information. Such ecommerce businesses will also need to invest in a warehouse space to maintain all the inventory.

4. Private Labels and White Label:
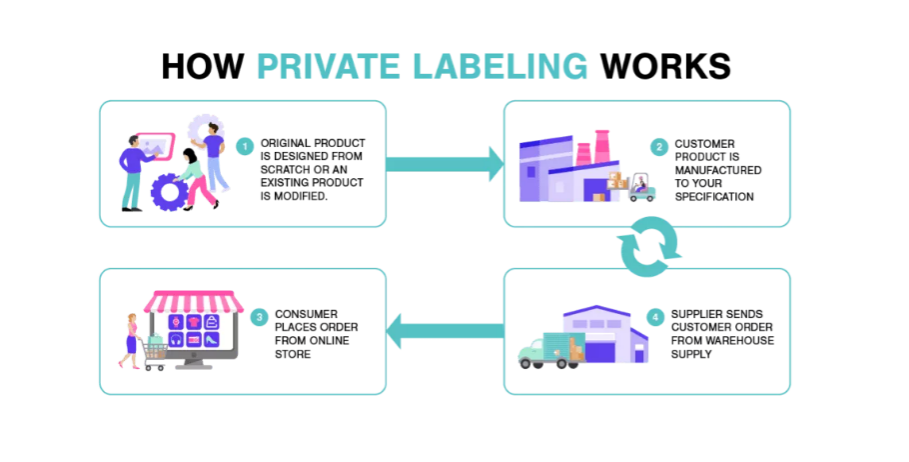
Private Label: Most new ecommerce entrepreneurs have exceptional product ideas but they have no resources or capacity to manufacture the products themselves. So, they reach out manufacturers in the market and get their product manufactured by them and then label, market and sell products under a private label. Recent projections suggest the ecommerce private label market will quadruple in the next 5 years to meet growing demands. Private-label brand owners own the design, specifications, production technique, and have exclusive rights to sell under a private brand.
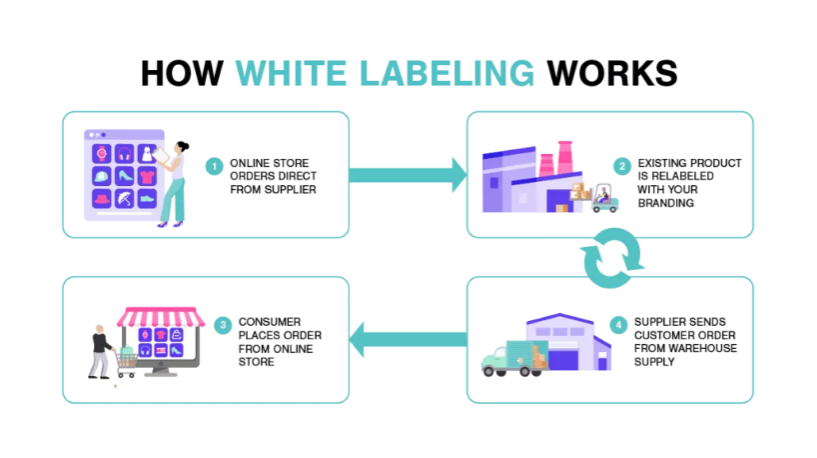
White Label: Just like the above-mentioned private label business model, white label retailers also apply their brand name on the products and resell the products purchased from a supplier.
This business model businesses are free from the management of manufacturing and quality control but deal with extensive competition. These vendors have control over the package design but not over product specifications and quality. Since any reseller can sell these products, competitors have minimal edge over their unique selling points and they have to use various marketing strategies and distribution channels to stand out in the crowd.
5. Subscription: With now-a days people being so occupied on the professional front – short on time, a meal delivery services who will deliver right at your door step is what anyone will be looking for. The beauty of and demand for convenience has given rise to the fast-growing subscription-service ecommerce revenue model.
A subscription business model allows customers to subscribe to a service for a fixed period ideally a month or a year. When the subscription expires customers can cancel or renew the same and enjoy the easy, benefits and cost savings on their orders.
The appealing advantages of this business model is tempting an ecommerce venture. Below are a few advantages:
- The owner of this business model enjoys high profit margins and low inventory risks
- The owners can plan the inventory and deliver the product in advance
- The owners can maintain high customer retention and loyalty by reducing order rates.
Looking at other business success model and failures of other business models will help in selecting the appropriate ecommerce business model for your company. This is an important decision any company will have to take before kick starting.
The most important thing is to understand the full picture and take the best decision well before time and also start somewhere and adapt along the way. Choosing an ideal model from the get go is… fitting, nevertheless, not to forget that as your business grows and develops you might want to change the business model which will help your business grow in numbers and adapt to change with time.